Imagine sending a text message to your friend while hiking deep in the mountains-no cell service, no internet. That’s what LoRa mesh networks do. This guide explains what they are, how they work, and why they matter for off-grid communication.
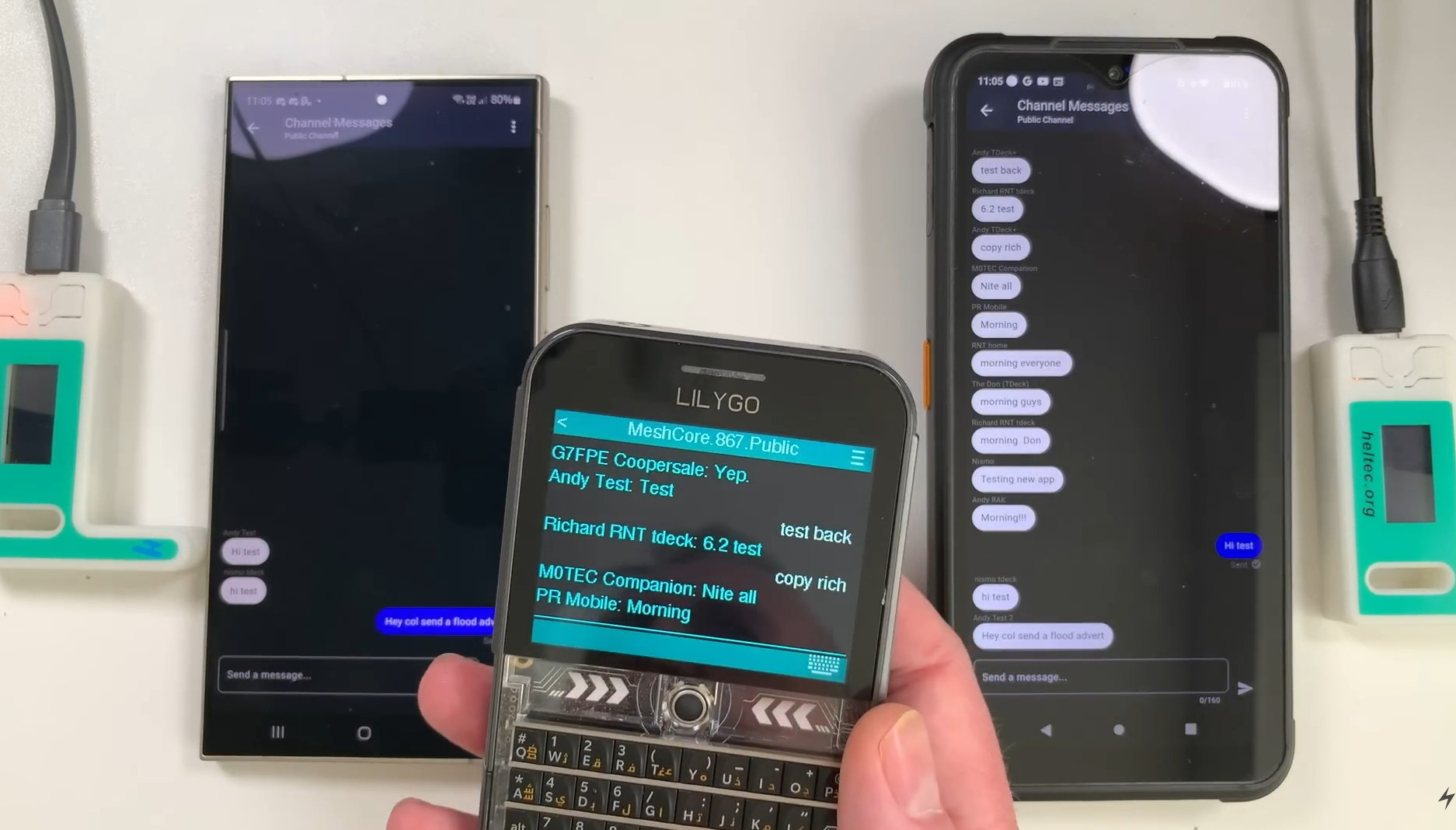 LoRa mesh devices enable off-grid communication without cell towers or internet. Image via CNX Software.
LoRa mesh devices enable off-grid communication without cell towers or internet. Image via CNX Software.
Off-Grid Communication Basics
“Off-grid” means operating without standard infrastructure like cell towers, Wi-Fi, or the power grid. Off-grid communication technologies let you stay connected when traditional networks are down or unavailable. Whether you’re camping in a remote area or preparing for emergencies, off-grid messaging ensures you can reach others without needing any existing network.
LoRa: Long-Range, Low-Power Radio
LoRa (short for “Long Range”) is a wireless technology known for exceptional range and minimal power usage. LoRa devices transmit small amounts of data (text messages or GPS coordinates) across several kilometers while using very little battery. Unlike walkie-talkies or ham radios, LoRa operates in unlicensed radio bands in most regions, so you don’t need a special license. This makes it perfect for personal and hobby projects-affordable and accessible to anyone.
The catch: LoRa sends data slowly and in tiny packets. You won’t stream videos over LoRa, but it handles text messages, sensor readings, and location data well. Even with obstacles like trees or hills, LoRa signals often reach farther than Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. In open areas with line-of-sight (hilltop to hilltop), range of a few miles is common, and more under ideal conditions. LoRa lets you cover distance without draining your battery-crucial for off-grid use.
What Is a Mesh Network?
A mesh network is a network where each device (or “node”) connects to multiple other devices, not just a single central hub. Messages hop from device to device to reach their destination. If one path is blocked or a node goes offline, the message tries another path. This self-healing design makes mesh networks robust-there’s no single point of failure.
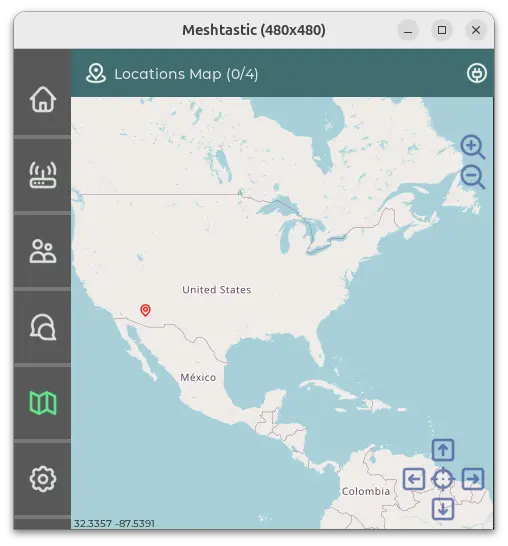 A mesh network map showing nodes and their connections. Image via Meshtastic.
A mesh network map showing nodes and their connections. Image via Meshtastic.
In a LoRa mesh network, each node acts as a relay for others, extending range beyond what any single device could cover on its own. If you and a friend are too far apart to communicate directly, a third node placed between you can pick up your message and forward it. The group of devices creates its own mini-network where everyone can send and receive messages, even if some members are out of direct radio range of each other. The more nodes you deploy (within reason), the larger and more reliable the mesh becomes.
Because mesh networks don’t depend on any central cell tower or router, they’re ideal for off-grid scenarios. Each node you add increases coverage and reinforces the network’s resilience. If one path fails, the message finds another route. This is why mesh networks are often called “self-healing” and are popular for disaster recovery and emergency communications.
Why Use a LoRa Mesh Network?
LoRa mesh networks combine long-range capabilities with mesh networking resilience. Here are the key benefits:
Truly Off-Grid Operation: LoRa mesh devices talk directly to each other. You don’t need cell service, Wi-Fi, or satellites. Your network is completely independent and works anywhere-deep wilderness, during natural disasters, or at crowded events where cell networks are overloaded. If the internet or power grid goes down, your LoRa mesh keeps running.
Extended Range through Hops: Each device in a LoRa mesh can forward messages for others. This hop-by-hop transmission extends your communication range. A message can travel miles by hopping through intermediate nodes. Even if any one link is limited (1-2 miles), multiple hops via other nodes can connect users much farther apart.
Low Power, Long Battery Life: LoRa radios sip power, making them ideal for battery-operated gadgets in the field. Many LoRa mesh nodes run for days or weeks on a battery. This makes them practical for outdoor adventures or emergency kits where charging options are limited. Some devices can be solar-powered for indefinite use.
Privacy and Security: LoRa mesh platforms like Meshtastic and MeshCore support encryption out of the box. Messages can be encrypted end-to-end, meaning outsiders can’t easily eavesdrop on your off-grid conversations. Since your messages aren’t going through any corporate server or cell tower, you control who’s listening.
Cost-Effective: Setting up a LoRa mesh is relatively inexpensive. The radios and devices are affordable (cheaper than satellite phones or long-range commercial radios). There are no monthly fees or subscriptions-once you have the gear, it’s free to use your mesh network.
Popular Uses for LoRa Mesh Networks
LoRa mesh networks have a growing community and variety of use cases:
Outdoor Adventures: Hikers, campers, hunters, and skiers use LoRa mesh gadgets to stay in touch when exploring remote areas with no cell coverage. A group on a backcountry hike can send text updates or GPS coordinates to each other over miles of wilderness. It’s a safety tool as well as convenience.
Emergency and Disaster Relief: When hurricanes, wildfires, or earthquakes strike, communication networks often fail. LoRa mesh devices can be rapidly deployed by emergency responders or community volunteers to coordinate rescue efforts. They provide a lifeline for messaging when phones and internet are down. Neighborhoods can set up LoRa mesh nodes for community emergency preparedness.
Off-Grid Living: In rural or remote off-grid homes, people use LoRa mesh to stay connected with neighbors or family nearby without needing infrastructure. Boaters use it to chat ship-to-ship, and campers in RVs use it in areas with no cell service.
Events and Festivals: At large outdoor events (music festivals, rallies, etc.), cell networks can become overloaded. Mesh devices let staff or attendees communicate reliably. Event organizers equip their team with LoRa mesh radios to coordinate security or logistics across a wide venue, independent of sketchy cell signals.
IoT and Sensor Networks: Beyond person-to-person messaging, LoRa mesh networks can carry data from sensors and IoT devices spread over a wide area. Environmental sensors in a forest (monitoring weather, animal movement, etc.) could use a LoRa mesh to send readings back to a central station. Low power means sensors run on battery for long periods, and the mesh can cover large properties or farms without new infrastructure.
Getting Started with LoRa Mesh
If you want to try a LoRa mesh network, the good news is it’s beginner-friendly. Projects like Meshtastic and MeshCore provide ready-to-use software for LoRa devices that turn them into mesh communicators.
 The Heltec V3 is a popular affordable LoRa device for mesh networking.
The Heltec V3 is a popular affordable LoRa device for mesh networking.
To start your own LoRa mesh you’ll need: a couple of LoRa-capable devices (small handheld radios or DIY boards), the mesh firmware (software) to load onto them, and a smartphone or laptop to interface for sending messages. With those, you can create a private network that keeps you connected anytime, anywhere, completely off the grid.
Check out our other guides to learn more about MeshCore vs Meshtastic, or browse our resources page for recommended hardware and tools!
Comments
Related Posts
RAK WisMesh 1W Booster vs RAK4631: Which WisBlock is Right for Your Mesh Network?
Technical comparison of the RAK WisMesh 1W Booster Starter Kit (RAK10724) and RAK4631 WisBlock Core for LoRa mesh networking. Compare RF power, range, power consumption, and expandability.
NanoVNA Antenna Testing Guide
Learn how to use a NanoVNA (H or H4 models) to test and tune your 915 MHz LoRa antennas for Meshtastic and MeshCore. Step-by-step guide covering unboxing, calibration, SWR measurement, and interpreting results.
EasySkyMesh: Power-Efficient MeshCore Firmware
EasySkyMesh delivers custom MeshCore firmware optimized for power efficiency, achieving 8-10mA idle current on repeaters. Learn why this matters for solar-powered nodes, sensor networks, and long-term mesh deployments.